Maintaining a medical office requires daily diligence to protect patients and staff. In Australia, healthcare cleaning standards call for targeted daily tasks and consistent infection‑prevention practices. This article outlines a practical checklist for General Practitioners and allied‑health clinics.
Key Principles
- Frequency: Tasks are categorised by how often they should be performed. The frequency is based on the risk level of the area and activity.
- Two-Step Process: All cleaning must follow a two-step process: first, physically remove dirt with detergent, and second, disinfect as required.
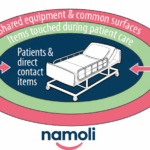
- Colour-Coding: Use a colour-coded system for cleaning equipment to prevent cross-contamination between different zones (e.g., Red for toilets, Yellow for clinical/infectious areas).
- Disinfectants: Use hospital-grade disinfectants listed on the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG) for all high-risk and high-touch areas.
Reception & Waiting Area
Patient‑facing spaces require constant vigilance. Reception counters, pens and sign‑in devices are touched frequently. Wipe down these surfaces at the start and end of each day with a TGA‑listed disinfectant. Chairs, armrests, door handles and light switches should be disinfected at least once daily and after any visible soiling. Vacuum or mop floors using a neutral detergent solution. Ensure reading material or toys (if provided) are cleaned daily or removed entirely to reduce transmission risk.
| Task | Daily (Start/End of Day) | Multiple Times Daily (High Traffic) | Weekly |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disinfect all high-touch surfaces | ✅ | ||
| Wipe down and sanitise desks, chairs, tables | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Tidy and sanitise children’s toys and books | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Empty and sanitise all waste bins | ✅ | ||
| Mop or sweep floors | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Deep-clean floors (mop and polish) | ✅ | ||
| Clean and dust all windowsills and ledges | ✅ | ||
| Empty and sanitise recycling bins | ✅ |
Consultation & Examination Rooms
These rooms see the highest turnover of patients. Clean exam tables, stools, counters and sinks between each patient using disinfectant wipes. At the end of the day, sanitise the entire room, including light switches, monitor buttons, keyboards and door handles. Use disposable barriers where appropriate (e.g. paper bed coverings). Maintain hand‑sanitiser dispensers at the entrance and within the room.
| Task | Between Each Patient | Daily (End of Day) | Weekly |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disinfect all high-touch surfaces | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Clean and sanitise examination tables & chairs | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Disinfect reusable medical equipment | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Disinfect all countertops and sinks | ✅ | ||
| Mop or sweep floors | ✅ | ||
| Empty and sanitise waste bins | ✅ | ||
| Dust all surfaces, shelving, and vents | ✅ |
Bathrooms & Amenities
Toilets, sinks and taps are high‑risk areas and may need multiple daily cleans. Restock soap, paper towels and alcohol‑based sanitisers. Clean door locks, flush buttons and light switches with disinfectant wipes. Empty bins regularly and line them with new bags. Ensure adequate ventilation in bathrooms; ventilation helps reduce airborne transmission of pathogens.
| Task | Multiple Times Daily | Weekly |
|---|---|---|
| Clean and disinfect all toilets & urinals | ✅ | ✅ |
| Disinfect all sinks and fixtures | ✅ | ✅ |
| Wipe and sanitise countertops | ✅ | ✅ |
| Mop and disinfect floors | ✅ | ✅ |
| Restock soap, toilet paper, and paper towels | ✅ | |
| Empty and sanitise waste bins | ✅ |
Staff Rooms & Kitchens
Desks, phones, computer keyboards and communal kitchen areas can harbour germs. Wipe down these surfaces daily and encourage staff to maintain personal hygiene. Remove rubbish at least daily and clean general waste bins with a neutral cleaner if not visibly soiled or a disinfectant solution if visibly soiled. Provide clear guidelines for personal desk cleanliness and ensure shared fridges or microwaves are cleaned weekly.
| Task | Daily | Weekly |
|---|---|---|
| Wipe down all countertops | ✅ | |
| Clean and disinfect all sinks | ✅ | ✅ |
| Empty and sanitise general waste bins | ✅ | |
| Wipe down all appliances (microwave, fridge) | ✅ | |
| Empty and sanitise recycling bins | ✅ | |
| Thoroughly clean and disinfect inside of fridge | ✅ | |
| Mop or sweep floors | ✅ | ✅ |

Choosing a Professional Partner
Medical practices benefit from partnering with a specialist cleaning provider. Companies like Namoli Healthcare use hospital‑grade disinfectants, colour‑coded cloths and TGA‑approved products to meet Australian healthcare standards. We develop risk‑based cleaning schedules, train staff in infection control and perform routine audits to ensure compliance. By outsourcing to professionals, clinics free up time for patient care while maintaining a safe environment.
Related Posts
Maintaining a safe, clean environment in aged care facilities is essential for protecting residents, supporting staff, and meeting regulatory requirements….
Terminal cleaning—conducted after surgical sessions or patient discharge—ensures operating rooms are safe for the next case. Though the CDC (U.S.)…
What Do Hospitals Use to Clean? Maintaining hygiene in hospitals is non-negotiable. Every surface, tool, and process must meet strict…